Measuring employee engagement
can be a challenging task since it’s an activity that requires evaluating of
human feelings and emotions (Robinson
et al., 2004). The most commonly used tool for measuring employee
engagement is an employee engagement survey. These surveys help gauge the
intensity of employee engagement as well as evaluate the relationships between
engagement and key business results. The findings from such surveys often
provide critical information on the effectiveness of HR practices of the
organization and provide insights on where changes are needed (Vance, 2006).
The surveys are usually conducted
online. The guarantee of anonymity is a very important aspect of the surveying
methodology – the employees will share their candid feedback only if they are
certain that the survey ensures anonymity. At my current organization, tools at
surverymonkey.com is used to send out the employee satisfaction surveys and the
responses are not tracked with complete anonymity guaranteed hence as an employee
I feel safe in sharing my honest opinion.
It is critical that an
employee engagement survey contains questions that would help capture the
essential data relating to the responder’s biographical characteristics
(gender, age, ethnicity to name a few) and other job-related characteristics
(such as department, length of service group, nature of employment). This
information is critical when it comes to the analysis of the responses and
coming up with strategies to increase employee engagement levels (Robinson et al., 2004). However, it
must be noted that these identifying questions should not break the anonymity
of the responder. For example, if the IT department of an organization only has
one employee, the survey should be designed in a way that the employee from IT
can remain anonymous.
The questions on employee
engagement surveys are often literal statements where the employees can pick an
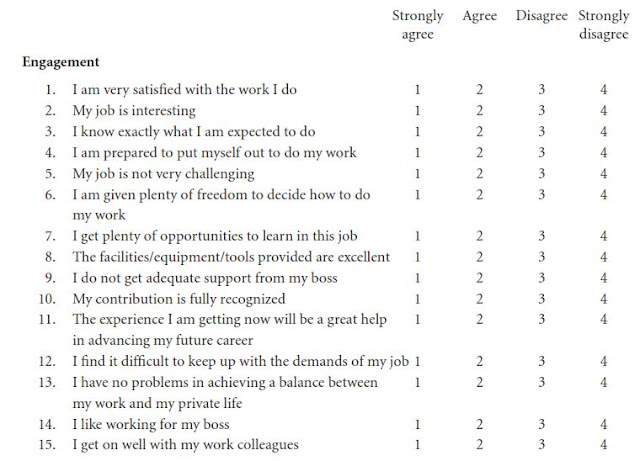
option from “Strongly disagree, Disagree, Neutral, Agree or Strongly agree”. Figure
05 shows a sample layout for engagement survey with the rating scheme. The
scale on the sample doesn’t include an option for the responders to select
“Neutral”. It can be argued that the option to respond as “neutral” could help
differentiate a not-engaged employee from an engaged or actively disengaged
person discussed on the previous post of this blog.
Figure
05: Sample Employee Engagement survey.
Source: (Armstrong, 2009).
Figure 06 lists some examples of statements used on
employee engagement surveys by reputed organizations. As seen with the
statements used by Dell Inc., the statements should be simply worded, specific
and relatable for the employee.
Figure
06: Sample questions for Employee Engagement surveys.
Source: (Vance, 2006).
According to Vance (2016), the
below are some of the key areas that the statements/questions on an engagement
survey should cover:
1.
Pride
in employer
2.
Satisfaction
with employer
3.
Job
satisfaction
4.
Opportunity
to perform well at challenging work
5.
Recognition
and positive feedback for one’s contributions
6.
Personal
support from one’s supervisor
7.
Effort
above and beyond the minimum
8.
Understanding
the link between one’s job and the organization’s mission
9.
Prospects
for future growth with one’s employer
10. Intention to stay with
one’s employer
Due to their simplicity and
effectiveness, many organizations chose surveys as their method of gauging
employee engagement. Other means such as focus groups and one-on-one interviews
would also be helpful in measuring employee engagement and diagnosing related
issues (Armstrong, 2009).
At my current workplace, a
bi-annual survey is shared with all employees. The survey has most of the
characteristics discussed on this post. The HR team of the organization also
conducts interviews with focus groups. The management team most of the time
uses the feedback received via surveys and discussions to make sure that
necessary adjustments are made on the company’s HR strategies & other
policies/procedures. These practices have helped the organization get
recognized as one of the best places to work in Sri Lanka in 2019, by Great
Place to Work Sri Lanka ® Institute.
Bonus fact: Interesting point to note is that carrying out employee
engagement surveys itself could also enhance employee engagement. This is
because, by asking for employees’ opinions/feedback and then implementing
strategies based on those survey results, the organization conveys the message
to its employees that their input is respected (Vance, 2006).
References:
Armstrong, M. (2009). Armstrong's handbook of human resource management
practice. 11th ed. London: Kogan Page, P. 1019.
Robinson, D., Perryman, S. and Hayday, S. (2004). The Drivers of Employee
Engagement. 1st ed. Brighton: Institute for Employment Studies, pp.13-20.
Vance, R. J. (2006) Employee Engagement and Commitment. [Online]
Available at: https://www.shrm.org/hr-today/trends-and-forecasting/special-reports-and-expert-views/Documents/Employee-Engagement-Commitment.pdf
[Accessed 01 October 2019].